
Minor Magnetic Storm Watch Issued -- Northern Lights Show Possible
Charged Particle Cloud from Sun heading towards Earth
When does the Aurora storm watch begin?
Details and Northern Lights Viewing Tips
By JIM THOMAS -- Soft Serve News, Posted: January 31, 2014
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Space Weather Prediction Center has issued a 24 hour minor magnetic storm watch indicating a Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) emanating from the Sun may be heading towards Earth. A CME is a fast moving cloud of charged particles which can cause a Northern Lights display.
The watch begins at the time indicated above. It should be noted that the beginning of the storm watch does not necessarily predict the arrival time of the CME cloud, rather it indicates that, within that 24 hour period, increased activity is expected. Real-time Aurora Borealis forecasts can be obtained at the Aurora Borealis Forecast page at Soft Serve News.
If you'd like to be notified when another storm is about to occur, you can get your own personal Aurora Alerts by text, email or phone call.
NOAA estimates the CME currently headed towards Earth might produce a Kp number of 5, but that's never fully known until it hits Earth. NOAA’s Space Weather Operations Chief, Bob Rutledge has indicated “these minor storm watches (G1 storm with a 5 Kp predicted) are typically grey areas, where the long term track record shows there is a 50% chance that the predicted level will be reached.” A strong storm watch was issued a little over 3 weeks ago, however it did not result in any significant activity. Often these storm watches do not result in the predicted activity unfortunately.
Stronger CMEs can sometimes cause trouble for satellites and create problems with electrical grids by inducing currents as the CME cloud interacts with the magnetic field that surrounds the earth. It is this disturbance of the Earth's magnetic field that causes the Northern Lights. NOAA indicates that weak power grid fluctuations may occur.
The Northern Lights, also known as the Aurora Borealis, can range from a faint green glow on the northern horizon to a multicolored, full-sky display which can be one of the most beautiful and awe-inspiring scenes in nature.
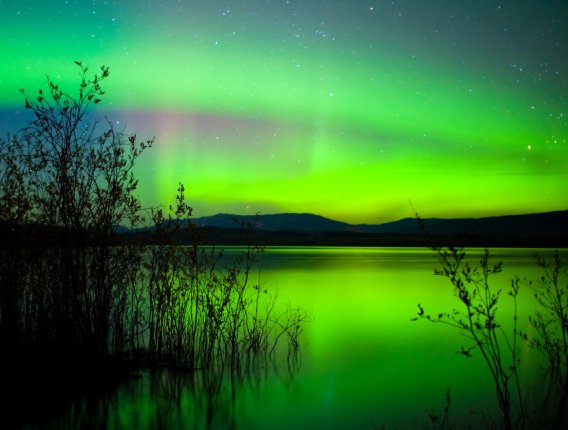

WILL YOU BE ABLE TO SEE THE AURORA?
To determine if you can see the Northern Lights use the following three steps:
Step 1 -- Know your Location's "KP number."
The KP number is the Geomagnetic Activity Level. The stronger the Aurora, the larger the KP number and the further south it can be seen. Find the KP number for your location on the one of the maps below. On the night you wish to view, periodically check the real-time Aurora Borealis Forecast. This will give you the KP number prediction for the Aurora for the next hour or so. If that number is greater or equal to the number on the map for your location, you're in luck. Even if the predicted number is one point too low, it still might be worth a look.
North America

Europe & Asia

Step 2 -- Check the Weather.
Auroras happen in the upper atmosphere, so if there are clouds blocking your view of the stars, you won't be able to see the Aurora.
Step 3 -- Shop for a Dark Spot.
Get away from those city lights. Darkness is best for viewing the Aurora. The fewer competing light sources, the better. But it is also very important to remember the widest part of the Aurora is when the sun is on the opposite side of the earth. So late, nighttime (or early morning) dark tends to be best.
EXPECTATIONS
Experienced Northern Lights hunters are familiar with disappointment. Predictions of when the CME cloud hits the earth are not always accurate. Sometimes CME events produce much smaller displays than expected, or even none at all. Also, it is possible the main auroral event happens during the day and therefore can only be enjoyed by people on the other side of the world where it's dark.
Even with these uncertainties, seeing the grandeur of a powerful Aurora Borealis display may be a once in a lifetime event, so for some it's worth the gamble to try.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Space Weather Prediction Center has issued a 24 hour minor magnetic storm watch indicating a Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) emanating from the Sun may be heading towards Earth. A CME is a fast moving cloud of charged particles which can cause a Northern Lights display.
The watch begins at the time indicated above. It should be noted that the beginning of the storm watch does not necessarily predict the arrival time of the CME cloud, rather it indicates that, within that 24 hour period, increased activity is expected. Real-time Aurora Borealis forecasts can be obtained at the Aurora Borealis Forecast page at Soft Serve News.
If you'd like to be notified when another storm is about to occur, you can get your own personal Aurora Alerts by text, email or phone call.
NOAA estimates the CME currently headed towards Earth might produce a Kp number of 5, but that's never fully known until it hits Earth. NOAA’s Space Weather Operations Chief, Bob Rutledge has indicated “these minor storm watches (G1 storm with a 5 Kp predicted) are typically grey areas, where the long term track record shows there is a 50% chance that the predicted level will be reached.” A strong storm watch was issued a little over 3 weeks ago, however it did not result in any significant activity. Often these storm watches do not result in the predicted activity unfortunately.
Stronger CMEs can sometimes cause trouble for satellites and create problems with electrical grids by inducing currents as the CME cloud interacts with the magnetic field that surrounds the earth. It is this disturbance of the Earth's magnetic field that causes the Northern Lights. NOAA indicates that weak power grid fluctuations may occur.
The Northern Lights, also known as the Aurora Borealis, can range from a faint green glow on the northern horizon to a multicolored, full-sky display which can be one of the most beautiful and awe-inspiring scenes in nature.

WILL YOU BE ABLE TO SEE THE AURORA?
To determine if you can see the Northern Lights use the following three steps:
Step 1 -- Know your Location's "KP number."
The KP number is the Geomagnetic Activity Level. The stronger the Aurora, the larger the KP number and the further south it can be seen. Find the KP number for your location on the one of the maps below. On the night you wish to view, periodically check the real-time Aurora Borealis Forecast. This will give you the KP number prediction for the Aurora for the next hour or so. If that number is greater or equal to the number on the map for your location, you're in luck. Even if the predicted number is one point too low, it still might be worth a look.


Step 2 -- Check the Weather.
Auroras happen in the upper atmosphere, so if there are clouds blocking your view of the stars, you won't be able to see the Aurora.
Step 3 -- Shop for a Dark Spot.
Get away from those city lights. Darkness is best for viewing the Aurora. The fewer competing light sources, the better. But it is also very important to remember the widest part of the Aurora is when the sun is on the opposite side of the earth. So late, nighttime (or early morning) dark tends to be best.
EXPECTATIONS
Experienced Northern Lights hunters are familiar with disappointment. Predictions of when the CME cloud hits the earth are not always accurate. Sometimes CME events produce much smaller displays than expected, or even none at all. Also, it is possible the main auroral event happens during the day and therefore can only be enjoyed by people on the other side of the world where it's dark.
Even with these uncertainties, seeing the grandeur of a powerful Aurora Borealis display may be a once in a lifetime event, so for some it's worth the gamble to try.
